What Is The B-matrix For The Identity Transformation I
Express the following equations in matrix equation and solve by finding the index coefficient matrix by elementary transformation method. Changing the b value leads to a shear transformation try it above.
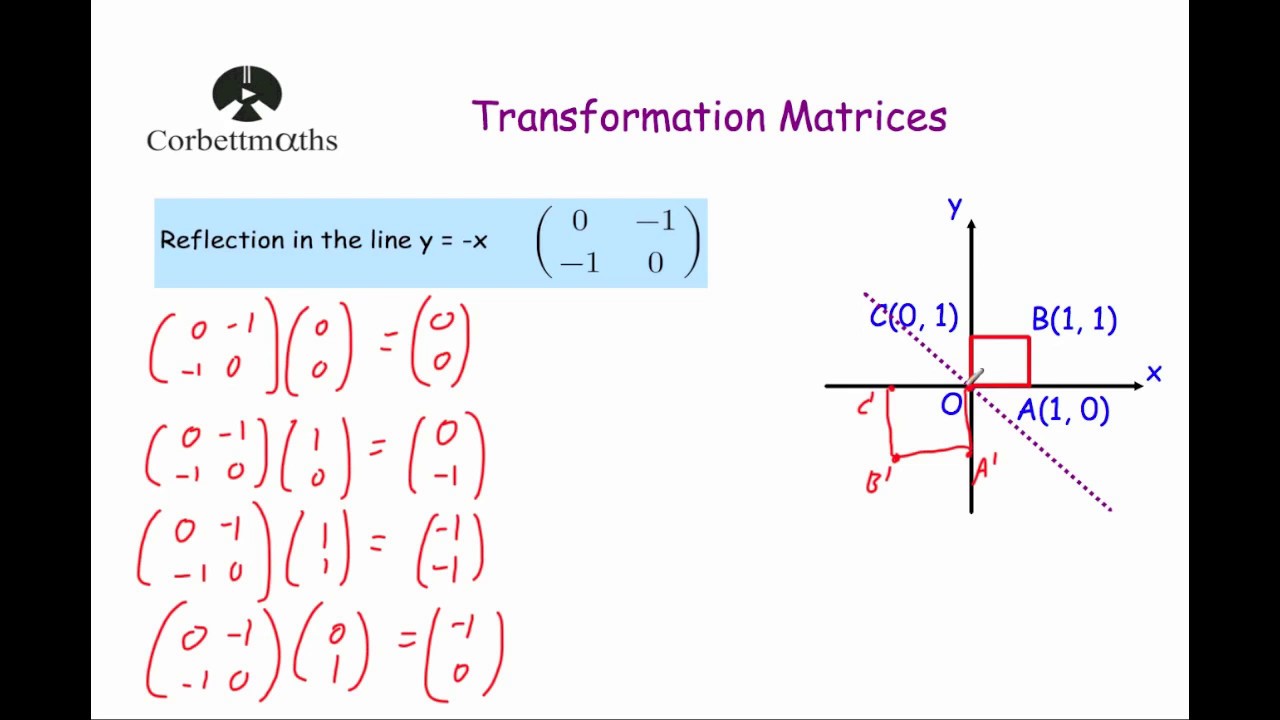
Reflection In The Line Y X Transformation Matrix Youtube
Similarly we say a linear transformation T.

What is the b-matrix for the identity transformation i. Let A be an m x n and let M be the matrix of TA with respect to bases B and B_. You will see that multiplication of matrices X and Y is only possible if the number of columns X the number of rows of Y Then if X is an a b matrix and B a c d. All of these True or False and Prove.
Using the equation for a transformation under a change of basis. U 0 n 1 u1 n 29 4 h h2 4 u0 n 1 25h 2 h2 4 1 25h 2 h2 4 u 1 n 1 u0 nh u1 n1 25h 2 h2 4 1 25h 2 h2 4 Before we look at the effect of h on the solution we show below the results obtained by taking a step size of h 01. And this one will do a diagonal flip about the.
When the transformation matrix abcd is the Identity Matrix the matrix equivalent of 1 the xy values are not changed. We defined some vocabulary domain codomain range and asked a number of natural questions about a transformation. If T is invertible then the matrix of T is invertible.
333 Let B and B be ordered bases for R where B B. True they have the same rank. Matrix multiplication is defined in this way.
I see my mistake. The special transformations Λ that can be reached continuously from the identity transformation of ℝ m n constitute the special pseudo-orthogonal group SOm n called the group of pseudo-rotations of signature m nA pseudo-rotation of signature m n is also called a Lorentz transformation of signature m nThe Lorentz transformation of signature 1 3 turns out to be the common. We will show that detA I D 0.
. Then the matrix of the identity transformation of R into itself with respect to B and B is the nxn identity matrix 1. Sal explains why the identity matrix is always a square matrix even though it works with non-square matrices.
Then there exists an mn matrix A such that Lx Ax for all. Find the B -matrix for the identity transformation I. You need to 1 first apply the transformation to each of the new basis vectors then 2 for each resulting basis vector change the basis to the new basis then 3 augment those into a new transformation matrix.
V1 V2 is linear if Lxy LxLy Lrx rLx for any xy V1 and r R. 337 Let A be an m X n matrix and let M be the matrix of TA with respect to bases B and B. The matrix of the identity transformation is I n.
Linear transformation standard matrix identity matrix. Rn Rm is a linear map. So the identity matrix is the unique matrix of the identity map.
We can find the general solution for when the transformation matrix is the same by setting A equal to B. Chapter 9 Matrices and Transformations 238 that This is the cost to household G if they get company 2 to deliver their milk. All eigenvalues lambda are D 1.
In Section 31 we studied the geometry of matrices by regarding them as functions ie by considering the associated matrix transformations. All vectors are eigenvectors of I. If A is the identity matrix every vector has Ax D x.
So in my example Step 1. For each xy point that makes up the shape we do this matrix multiplication. Most 2 by 2 matrices have two eigenvector directions and two eigenvalues.
Then the dimensions of the column spaces of A and M are equal. In college algebra we could perform a horizontal line test to determine if a function was one-to-one ie to determine if an inverse function exists. Change to the basis 2 which yields 1 in the new basis.
To prove it note that the identity transformation takes e i to e i and that these are the columns of the identity matrix. Then the matrix of the identity transformation is the n x n identity matrix I. Because thats the identity matrix thats the property of the entity matrix and of course C we already know is an a by B matrix a rows and B columns and B columns now what are going what based on.
This is unusual to say the least. What is the B -matrix for the identity transformation I. Matrix transformations Theorem Suppose L.
Convert 1 2 1 3 into an identity matrix by suitable row transformations. The matrix is the nn identity matrix. Given vector spaces V1 and V2 a mapping L.
Any scalar matrix which is a scaled identity matrix will have this property. Then 4 apply that to the vector expressed in the new basis. Using Cramers rule the solution is obtained as.
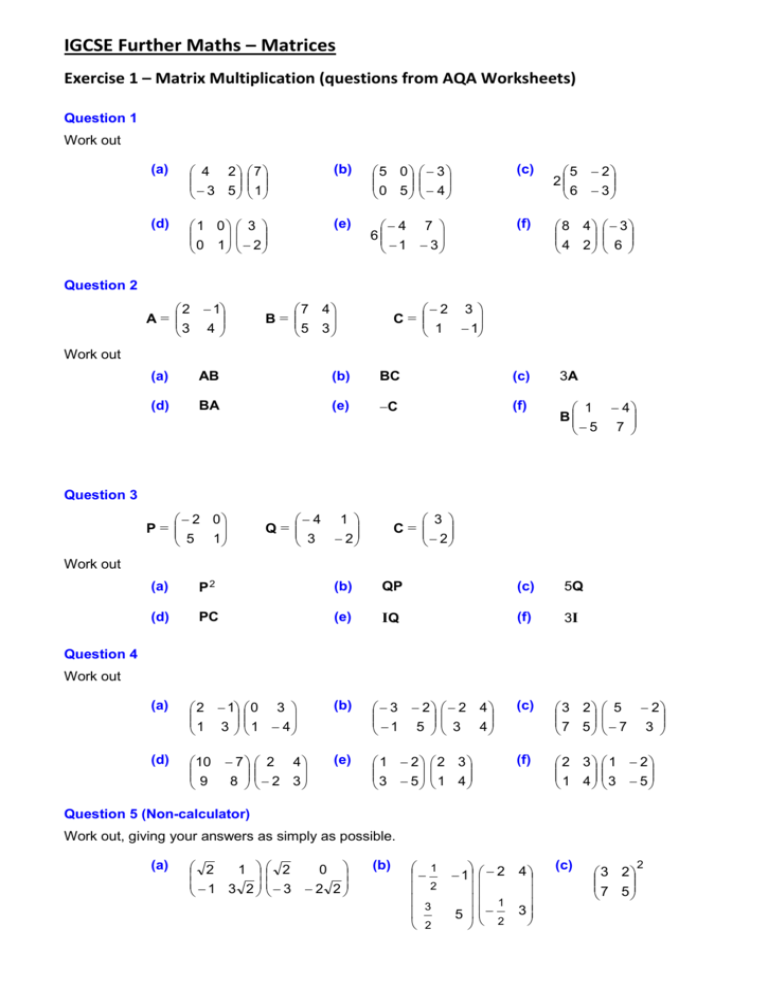
Igcse Further Maths Matrix Transformations Worksheet
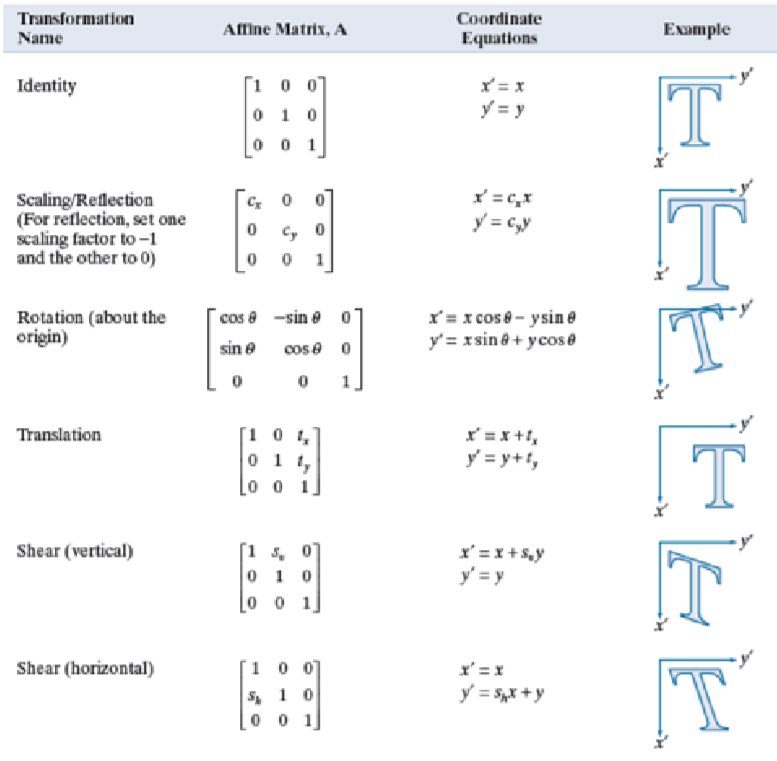
Consider Table 1 Below Which Shows The Matrices For Chegg Com
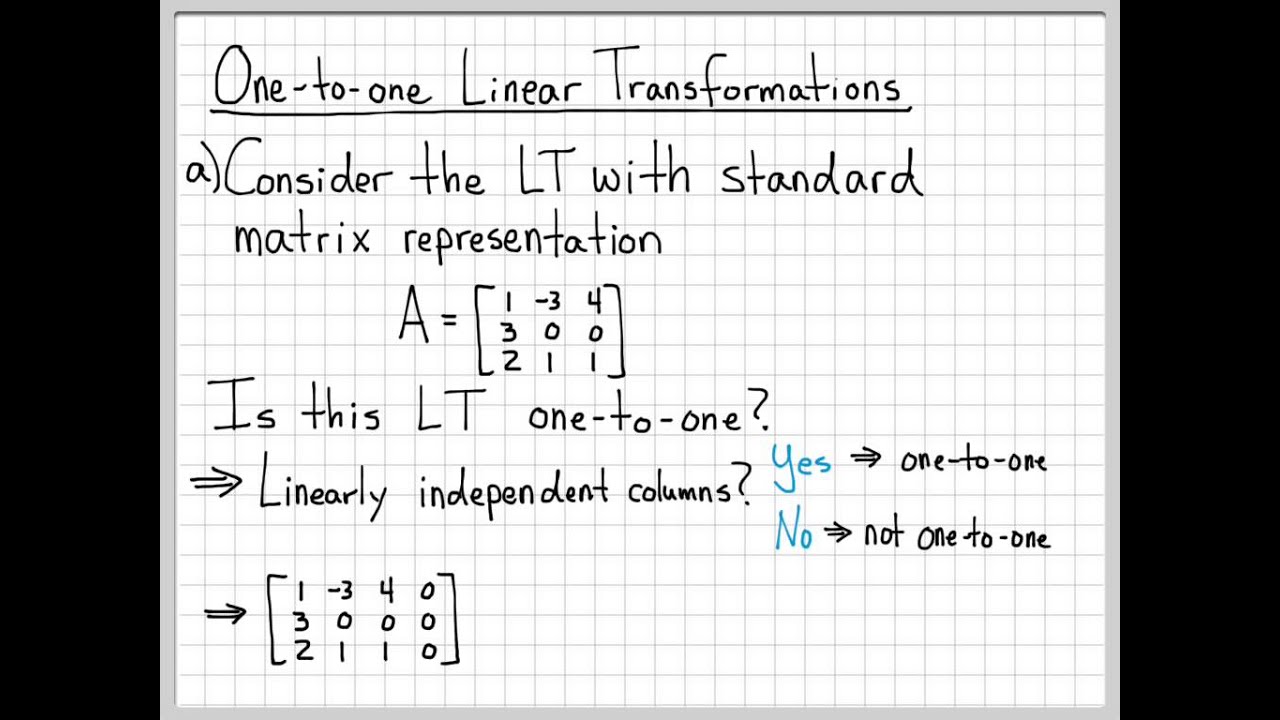
Linear Algebra Example Problems One To One Linear Transformations Youtube

Fp1 Matrices Transformations Ppt Download
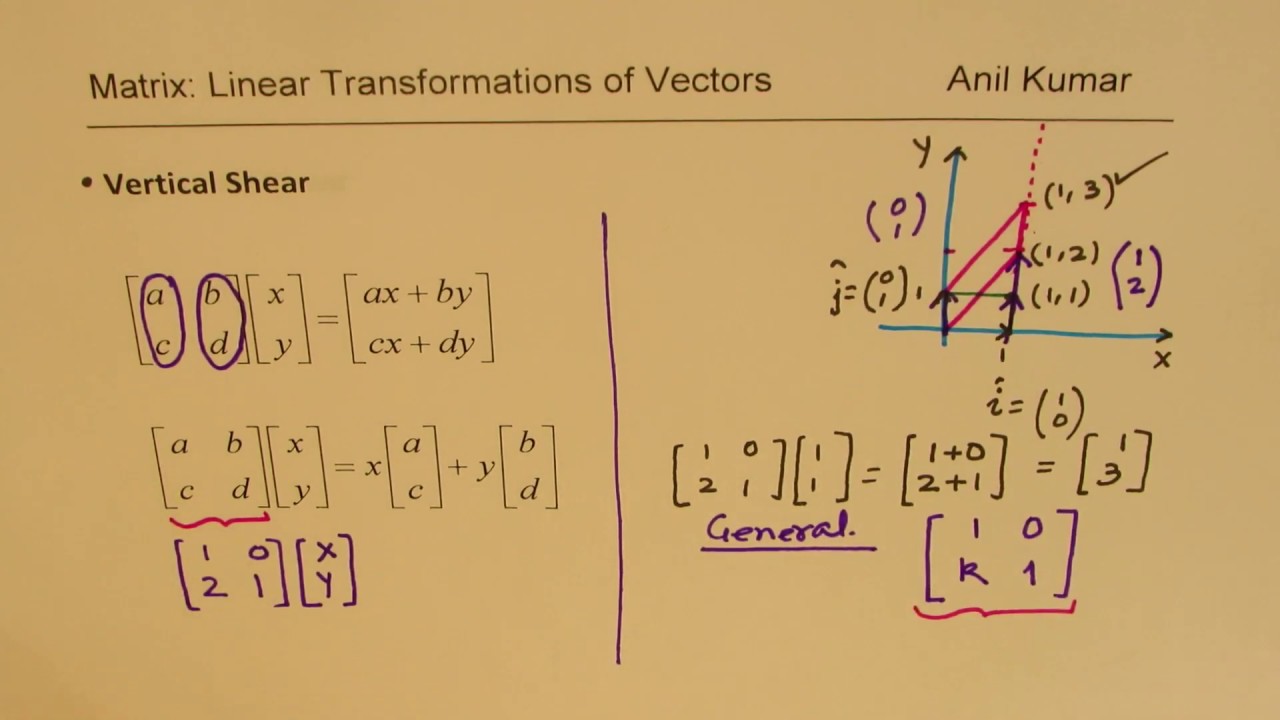
Linear Transformations Vertical And Horizontal Shear With Matrices Algebra Youtube
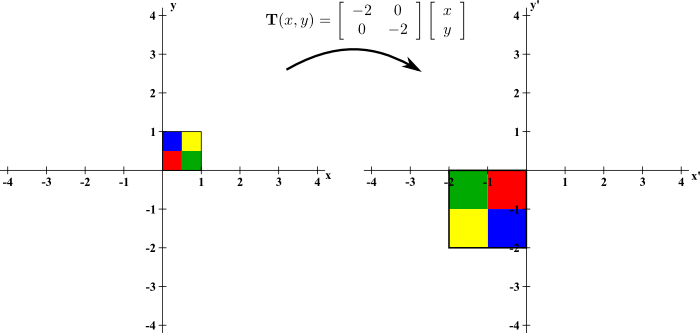
Determinants And Linear Transformations Math Insight

Sections 1 8 1 9 Linear Transformations Ppt Video Online Download
Http Web Yonsei Ac Kr Hgjung Lectures Mat203 06 20linear 20transformations Pdf
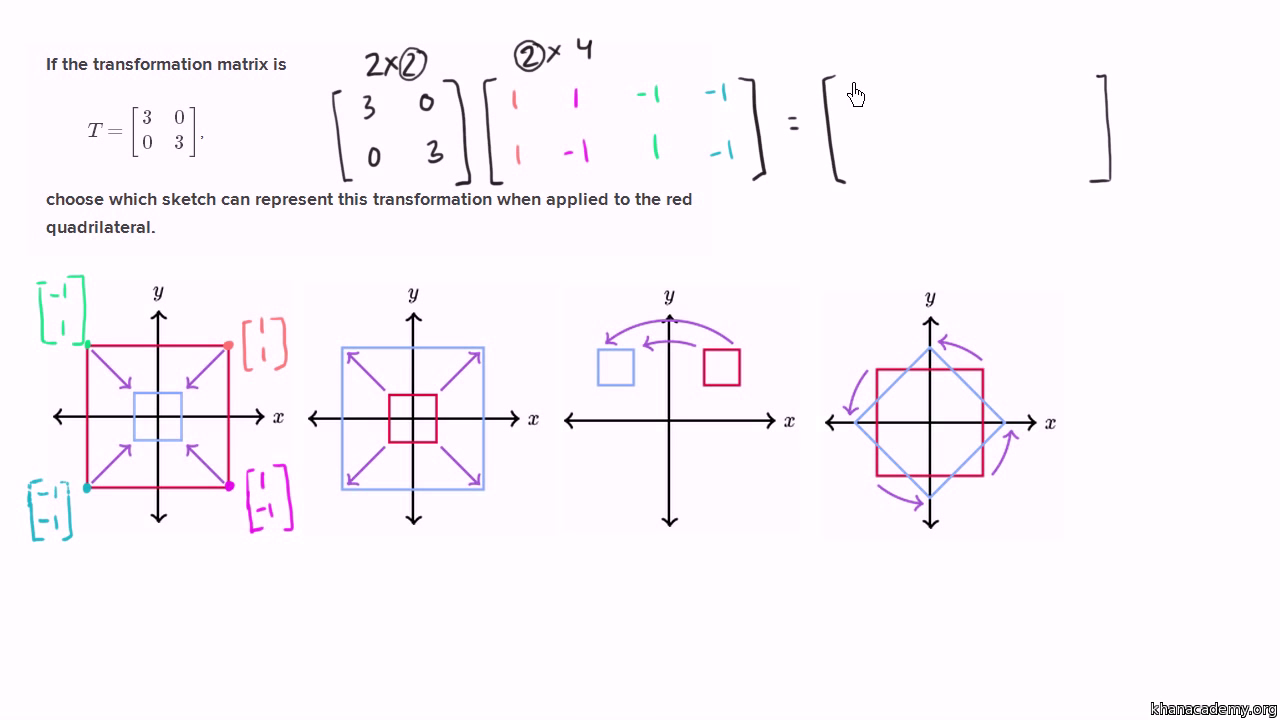
Visual Representation Of Transformation From Matrix Video Khan Academy

Reflection Transformation Matrix







